Here is a comprehensive guide to industrial laser marking machines, designed to help you make an informed investment decision. This guide covers core technologies, key considerations, market trends, and a practical framework for selection.
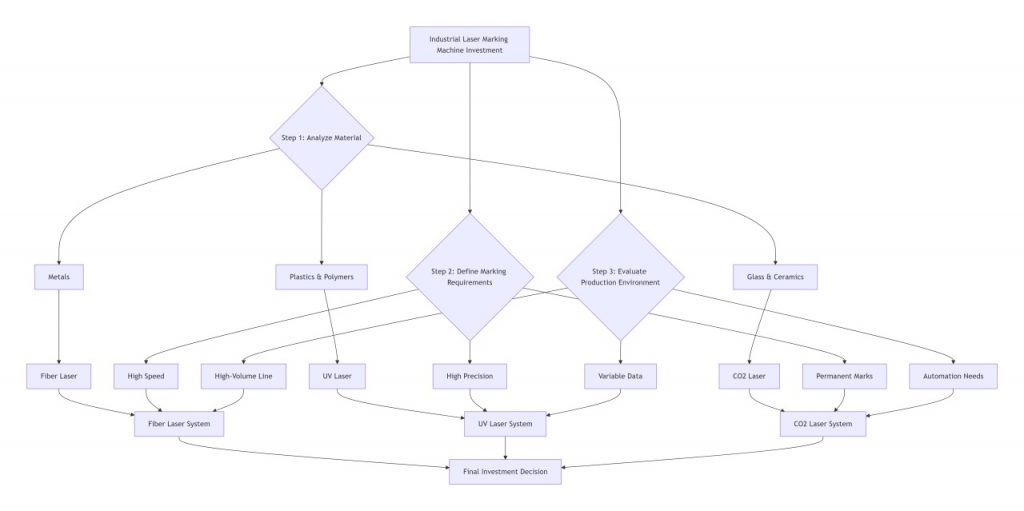
flowchart TD
A[Industrial Laser Marking Machine Investment] --> B{Step 1: Analyze Material}
A --> C{Step 2: Define Marking Requirements}
A --> D{Step 3: Evaluate Production Environment}
B --> B1[Metals]
B --> B2[Plastics & Polymers]
B --> B3[Glass & Ceramics]
B1 --> B4[Fiber Laser]
B2 --> B5[UV Laser]
B3 --> B6[CO2 Laser]
C --> C1[High Speed]
C --> C2[High Precision]
C --> C3[Permanent Marks]
D --> D1[High-Volume Line]
D --> D2[Variable Data]
D --> D3[Automation Needs]
B4 & C1 & D1 --> E[Fiber Laser System]
B5 & C2 & D2 --> F[UV Laser System]
B6 & C3 & D3 --> G[CO2 Laser System]
E & F & G --> H[Final Investment Decision]1. Core Laser Technologies: Matching the Laser to Your Material
The most critical decision is choosing the right type of laser, as its wavelength determines how effectively it interacts with your specific material.
- Fiber Lasers: These are the workhorses for metal marking. With a wavelength of 1064 nm, they are highly absorbed by metals and are ideal for creating permanent marks on stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. They are prized for their reliability, long service life (often over 100,000 hours), and low maintenance needs.
- CO2 Lasers: Operating at a longer wavelength (10.6 μm), these are best suited for non-metal materials. They excel at marking and engraving wood, acrylic, glass, leather, paper, and many plastics. They are often a more cost-effective solution for these organic materials.
- UV Lasers: This is the go-to technology for using a 355 nm wavelength for “cold marking” on sensitive materials. The high-energy photons break molecular bonds without generating significant heat. This makes them perfect for plastics, silicon wafers, glass, and medical devices, preventing burning, melting, or micro-cracks. They are also essential for ultra-fine marking in microelectronics.
Pro Tip: If you work with a wide variety of materials, some suppliers offer hybrid systems or configurations with multiple laser sources to cover all your needs.
2. Key Investment Considerations: Beyond the Laser Type
Once you’ve identified the suitable laser technology, evaluate these critical factors to ensure the system meets your operational and financial goals.
- Marking Requirements: Define your needs for speed, precision, and mark permanence. High-volume production lines require fast scanning heads, while industries like medical devices demand micron-level accuracy. Laser marks are permanent and resistant to wear, fading, and chemicals, which is crucial for traceability.
- Software and Integration: The software is your control center. Look for systems compatible with industry-standard software like EZCAD that allow easy import of vector files (DXF, AI) and support for variable data (serial numbers, barcodes, QR codes). For automated production, ensure the machine can integrate with PLCs, MES, and vision systems.
- Operational Costs (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Factor in electricity consumption, cooling system needs, and potential spare parts. Unlike ink-based systems, lasers have no ongoing costs for inks or solvents, leading to significant long-term savings and a smaller environmental footprint.
- Supplier Support and Service: A reliable supplier is as important as the machine itself. Verify the availability of technical support, training, warranty, and spare parts. A machine breakdown without local support can lead to costly production halts.
3. 2025 Market Outlook and Innovative Applications
The industrial laser marking market is dynamic, valued at approximately $4.25 billion in 2022 and projected to grow steadily, driven by demand across the automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical sectors.
Staying ahead means understanding emerging trends:
- AI and Automation: AI-driven laser systems are revolutionizing smart factories. They can auto-adjust parameters in real-time for perfect marks on every part, drastically reducing scrap rates and optimizing energy use.
- 3D and Multi-Axis Marking: For marking curved or uneven surfaces (e.g., engine components, medical implants), 3D systems with dynamically adjusting focus lenses are becoming essential. They eliminate the need for complex jigs and provide consistent quality on complex geometries.
- Sustainability: Laser marking is a clean technology. It eliminates the need for inks, solvents, and chemicals, helping companies reduce waste and meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
Financial Planning and ROI
Justifying the investment requires a clear view of costs and returns. The table below outlines the primary financial considerations.
| Aspect | Considerations | ROI Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Machine cost, installation, operator training. | Increased production speed, reduced labor costs. |
| Operational Costs | Electricity, cooling, maintenance contracts, spare parts. | Elimination of consumables (ink, labels), reduced waste and rework. |
| Value-Added Benefits | Improved traceability, higher quality marks, compliance with regulations, brand enhancement. |
Typical Payback Period: Many businesses see a return on their investment within 6 to 18 months, thanks to productivity gains and lower operating costs.
Final Checklist Before You Buy
- ✅ Material Testing: Always provide your actual samples to the supplier for a marking test. This is the only way to verify the results.
- ✅ Production Match: Ensure the machine’s speed and uptime can meet your daily production volume.
- ✅ Software Check: Verify the software is user-friendly and compatible with your existing design and data systems.
- ✅ Support Verification: Choose a supplier with a proven reputation and readily available technical support and services.
- ✅ Budget for TCO: Account for both the initial investment and long-term operational costs.
By systematically analyzing your materials, production needs, and the total cost of ownership, you can select an industrial laser marking machine that not only meets your current demands but also scales with your business growth. This investment is a strategic step toward greater efficiency, quality, and competitiveness in the modern manufacturing landscape.
If you have any questions, contact us via WhatsApp for great solutions.











